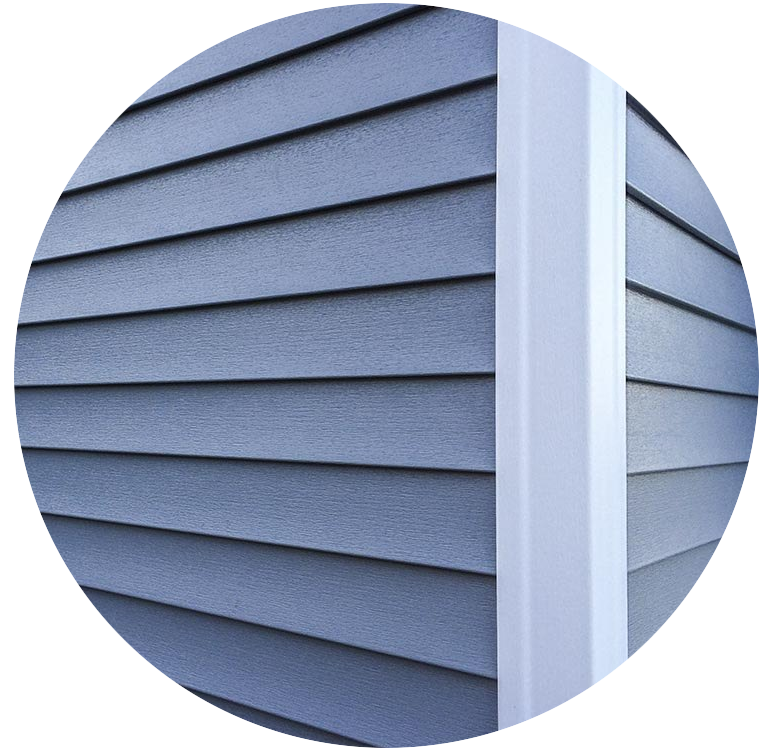
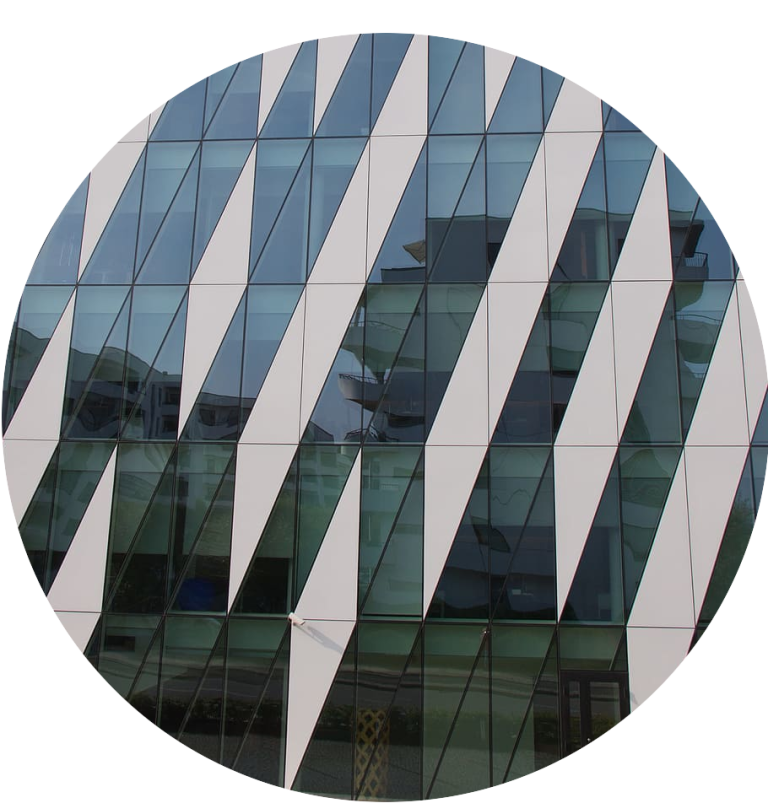
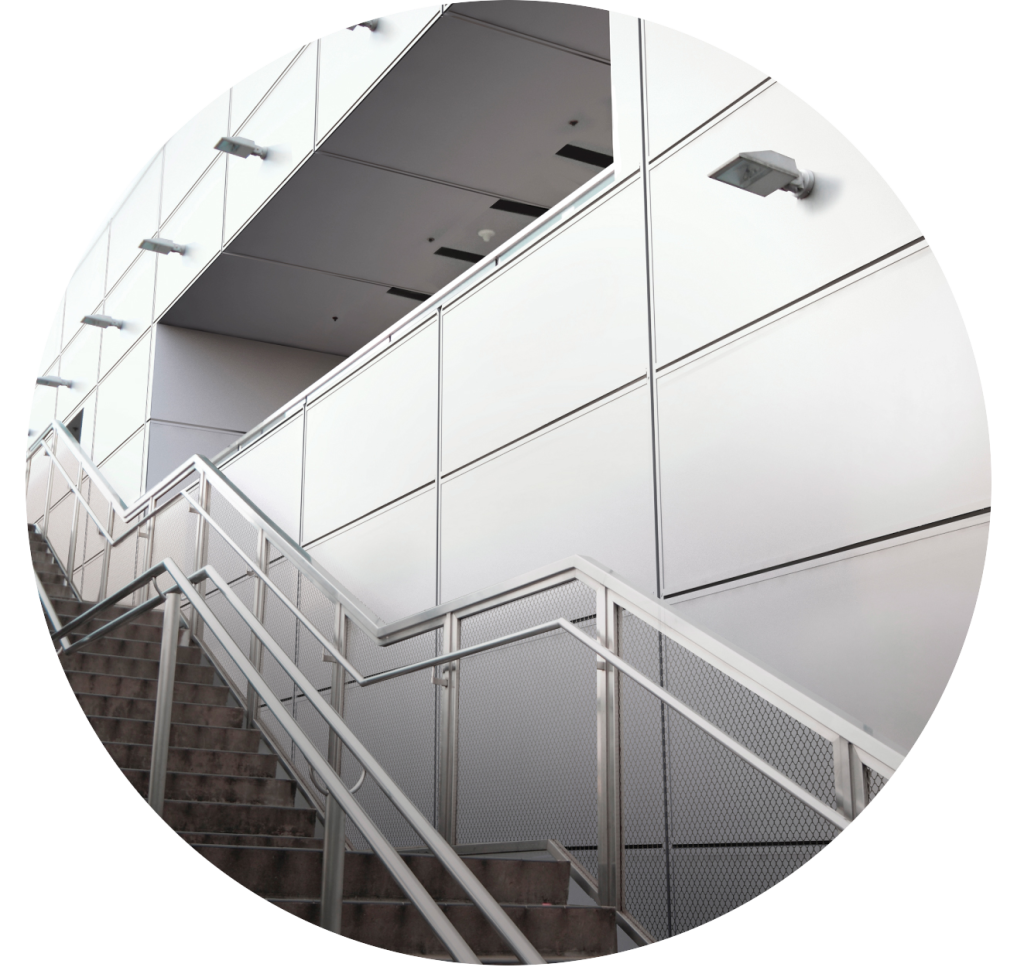
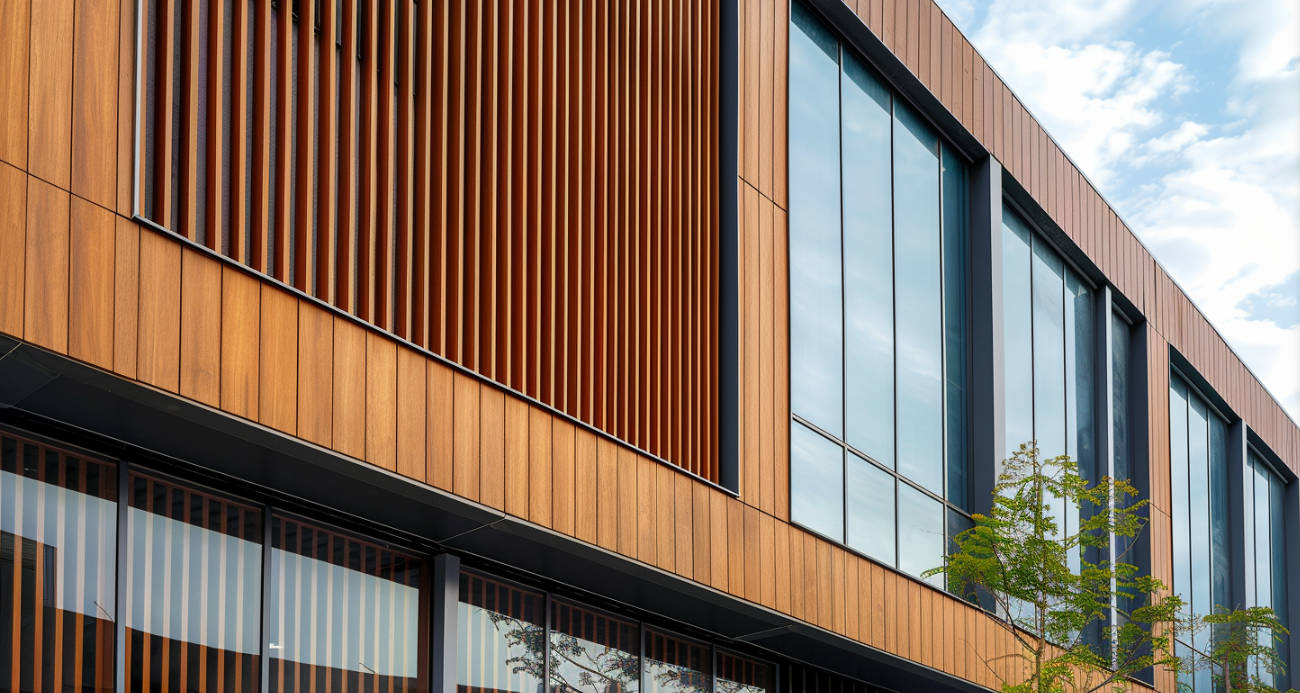
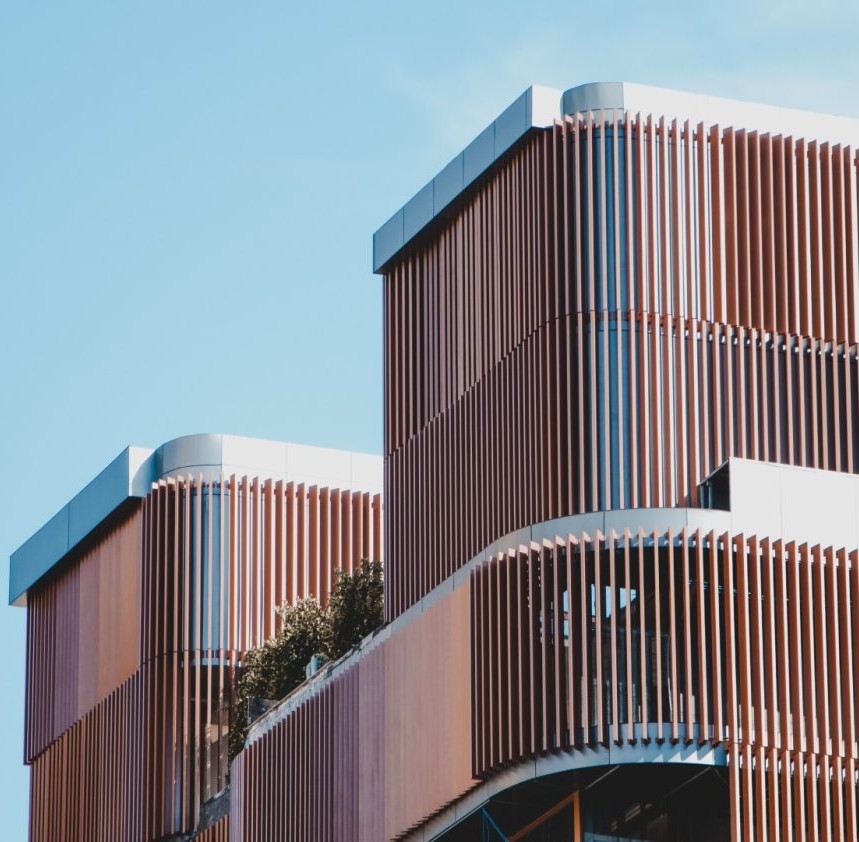
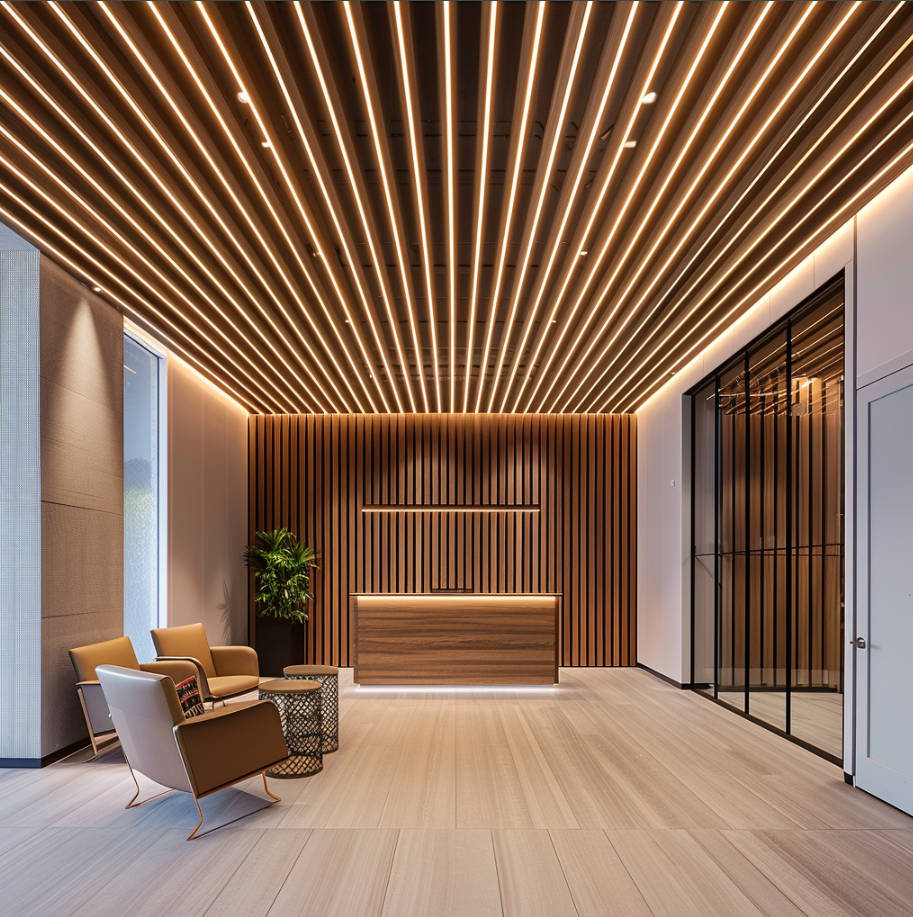
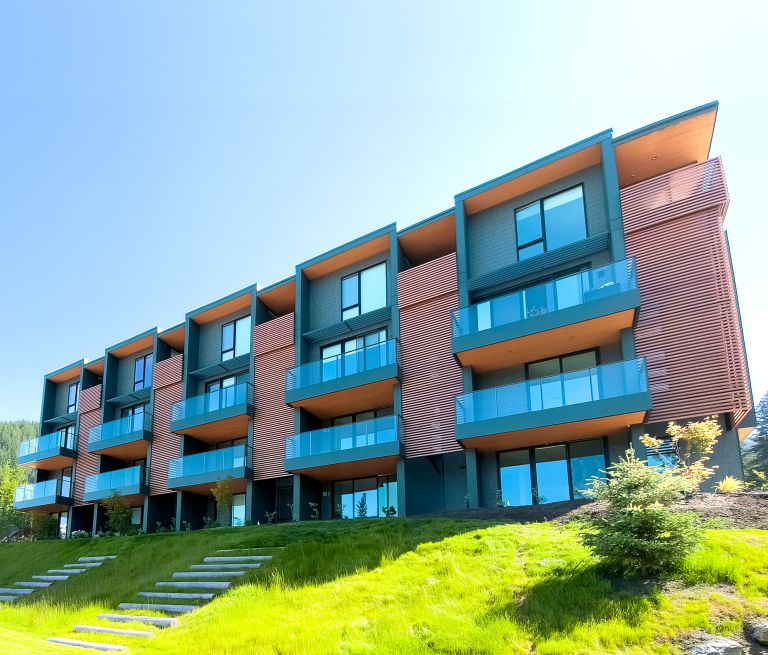
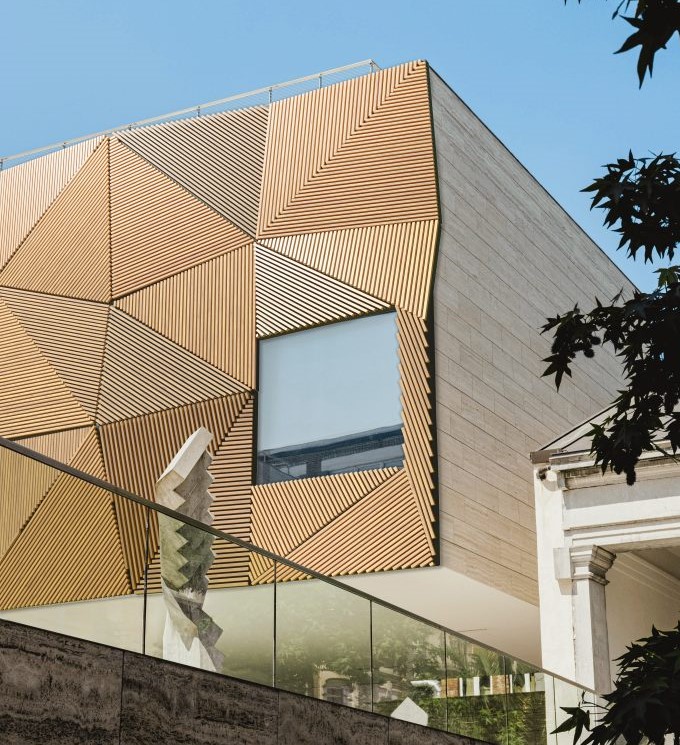
Material Selection Based on Climate and Environment: The choice of cladding material should align with the building’s geographical location. For instance, aluminum cladding offers superior resistance to corrosion in coastal areas, while stone or brick cladding may be better suited for regions with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Ease of Installation and Labor Efficiency: Time and labor efficiency are vital for project success. Modular systems are pre-engineered for quick assembly, reducing on-site installation time and minimizing the need for skilled labor.
Compliance with Building Codes and Standards: Cladding systems must meet stringent building codes, particularly regarding fire resistance and wind loads. ACM panels, for example, are fire-tested and compliant with industry standards, offering peace of mind for both designers and clients.
Budget Optimization and Cost Management: Cladding materials affect the overall budget through upfront costs, maintenance, and lifespan. Materials like aluminum composite panels (ACM) are often preferred for their durability, requiring less maintenance and offering long-term value.
Why It Matters: For architects and engineers, cladding is not just about aesthetics; it’s a solution that influences a building’s performance, safety, and longevity. Thoughtful material selection and innovative systems empower professionals to create buildings that are not only beautiful but also efficient, sustainable, and compliant with industry standards.